χ-separation is an advanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) technique that generates maps of paramagnetic and diamagnetic tissues, potentially reflecting the distribution of the paramagnetic iron and diamagnetic myelin in the brain. This method has been applied in various studies of neurological diseases such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple system atrophy.
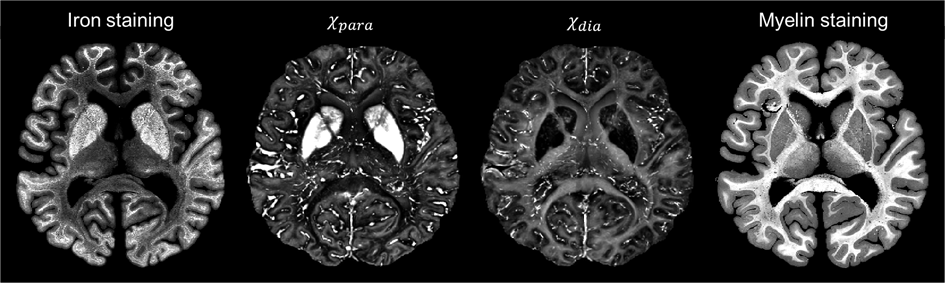
Taechang Kim, an exchange student from Seoul National University, South Korea, came to CUAS for a one-month research stay. His research focuses on the development of χ-separation and demonstration of its potential as a surrogate marker for iron and myelin. In the collaboration with Prof. Günther Grabner, Teachang aimed to validate χ-separation by quantitatively and qualitatively comparing the MRI susceptibility source maps with histological brain iron and myelin staining images.

The results showed statistically significant linear correlations between paramagnetic susceptibility values and iron staining optical density, as well as between diamagnetic susceptibility values and myelin staining optical density. Qualitative comparison revealed clearly delineated substructures in several brain regions such as the laminar structures of the globus pallidus and the subthalamic nuclei, within both the paramagnetic and diamagnetic susceptibility maps regions. However, some areas of high myelin concentration within the globus pallidus in the basal ganglia were not well represented in the diamagnetic susceptibility map. This discrepancy may highlight the need for further improvements in the χ-separation.
In the future, we plan to repeat this validation using χ-separation based on the gold standard COSMOS algorithm, by acquiring multi-orientation MRI data. This collaborative work is ongoing!!
Yours,
MedTech @ FH Kärnten